

Definition: What Qualifies as an AI Agent-
For this report, an AI agent is defined as:
● A system that autonomously executes multi-step tasks by reasoning, planning, and interacting with external tools or environments based on high-level natural language instructions.
● These agents typically use large language models (LLMs) + tool stacks to act on behalf of a user or workflow (e.g., web navigation, API calls, automation).
This distinguishes agents from simple prompt-based assistants — agents must complete tasks beyond text generation.
Context: Why the New Benchmark Matters-
Recent enterprise benchmarks (e.g., APEX-Agents) have simulated real professional workflows (consulting, banking, law). Early evidence suggests poor performance relative to human standards — even when underlying foundation models are strong. This challenges assumptions that agents can be plugged into knowledge work without substantial supervision or remediation.
| Benchmark | Purpose | Task Types | Key Metric |
| WorkBench | Realistic workplace task evaluation | Emails, scheduling, database actions | Task completion rate |
| VisualAgentBench (VAB) | Vision + language workflows | Object identification, visual planning | Success rate (% correct) |
| RE-Bench | Research & ML tasks | Kernel optimization, fine-tuning | Success rate vs expert |
| GDPval | Real household job tasks | Email, vendor planning, auditing | “Win rate” vs professionals |
| Domain-Specific Enterprise Benchmark (IT Ops) | Enterprise IT tasks | Issue resolution, accuracy & stability | Accuracy & pass |
Agent Performance by Benchmark-
| Benchmark | Avg. Agent Success Rate |
| WorkBench-Task Completion | 3% – 43% |
| VisualAgentBench | ~36% |
| GDPval Model Win Rate | ~47% (best) |
| Domain-Specific Agents (IT) | ~82% |
| RE-Bench (2-hr) | 4× human surrogate score |
| Capability | Supporting Metric | Benchmark |
| Short-Horizon Task Execution | Top agent ≈ human-level in 2-hr constrained tasks | RE-Bench (4× score) |
| Domain-Specific IT Operations | ~82.7% accuracy | Enterprise IT Benchmark |
| Basic Workflow Steps | Agents can interact with tools | WebArena partial success |
Key Quantitative Insight-
● On enterprise IT ops, domain-specific agents outperform general LLM agents in accuracy (82.7%) and stability — defined as consistency across repeated runs.
These cases reflect tasks that are bounded, structured, and narrow, especially when agents have pre-built domain knowledge.
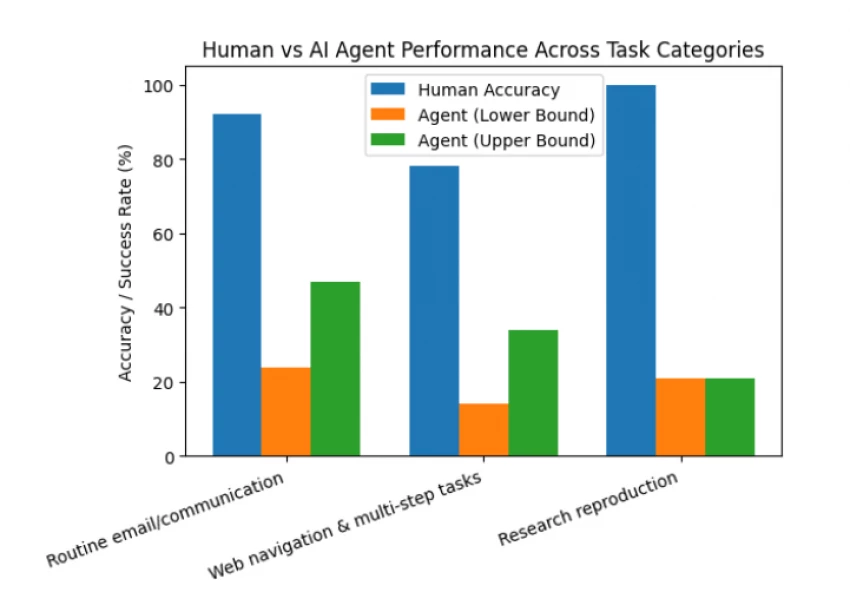
| Task Type | Human vs Agent | Agent Score |
| General human queries | ~90% human accuracy | ~15–24% agent |
| Multi-tool, multi-domain workflows | Humans >> agents | ~24% task completion |
| Real research reproducibility | Humans >> agents | ~21% best agent |
Examples with Data
● WorkBench: GPT-4 completes only 43% of tasks, with many errors like sending emails to wrong recipients.
● VisualAgentBench: Best model achieves 36.2% success, average ~20% among field models.
● GDPval: Best agent wins ~47.6% of time vs professionals — below majority reliability.
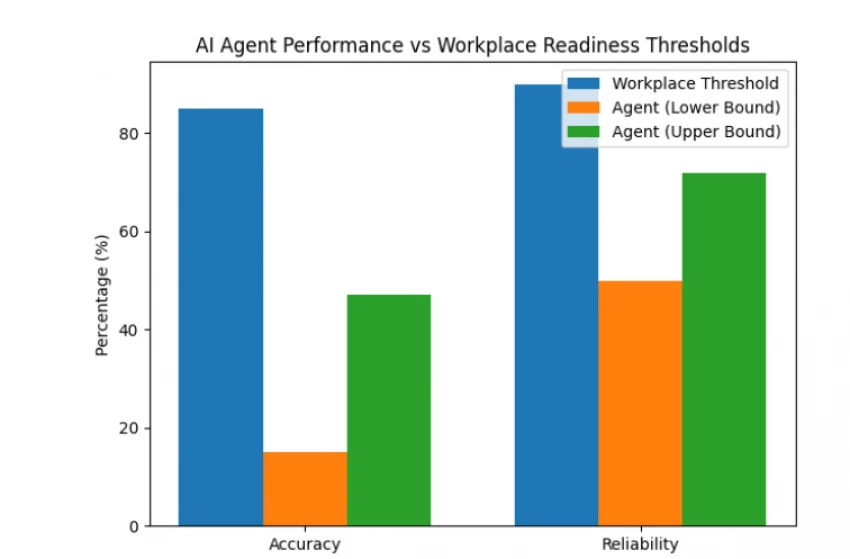
To quantify “workplace readiness,” we define measurable thresholds:
| Criterion | Minimum Acceptable Threshold | Agent Performance |
| Task Accuracy | ≥ 85% | 15–47% (varies by task) |
| Reliability | Consistency > 90% | 50–72% (domain-specific best) |
| Latency | < 2s for fast interactions | ~2.1s in the best IT agent |
| Cost Efficiency | ROI positive within budget | Varies widely |
| Integration Quality | Seamless tool chaining | Partial/brittle |
Interpretation:
Agents often fail to meet workplace thresholds on accuracy and reliability for general tasks. Domain-specific optimization improves performance but remains context-limited.
| Metric | Before Agent | After Agent |
| Avg. response time | 8hrs | 2.1s (automated responses) |
| Accuracy | 55% | 82.7% |
| Cost per task | High human cost | Lower automated cost |
Note: Success here correlates with domain specialization, not general workplace ubiquity.
| Metric | Human | Best AI Agent |
| Reproducibility success | ~100% | ~21% |
| Time to completion | Varies | Minimum |
| Decision quality | High | Low |
This highlights systemic weakness: agents struggle with novel, unstructured reasoning common in advanced work roles.
Documented failure modes:
| Failure Type | Impact | Source |
| Hallucinations | Wrong output confidently asserted | Benchmarks |
| Context loss | Missing cross-domain history | GDPval findings |
| Brittleness | Fails in minor environment changes | WebArena |
| Cost vs quality | High cost per task | ROI concerns |
Real workplace deployment also encounters:
● Security & integration gaps.
● Data governance & compliance challenges.
● Lack of robust enterprise debugging tools.
Synthesis
● Agents exceed baseline on narrow, structured tasks.
● Agents operate below readiness thresholds for complex, multi-step, real work.
● Domain expertise improves success, but general readiness is not yet achieved.
Key Evidence Supporting Doubts-
● Benchmarks show agent success rates well below human standards (15–47% across general tasks).
● Agents fail complex task combinations, multi-domain reasoning, and reproducibility tests at scale.
● Even with domain specialization, performance improves only in narrow workflows, not generalized workplace application.
Where Progress Exists-
● Domain-specific agents can meaningfully automate technical workflows (e.g., IT ops).
● Short-horizon tasks (under structured constraints) see better performance.
Overall Answer-
No — AI agents are not yet broadly ready for general workplace deployment.
Current performance falls short of critical readiness thresholds, especially for unstructured, multi-domain, and high-impact professional tasks.
● Stanford AI Index Report 2025 — agent success rates; top model ≈36.2% average.
● WorkBench Benchmark — agents complete 3–43% of tasks.
● GDPval real work tasks — best models <50% performance vs professionals.
● Enterprise IT agent benchmark — domain-specific agents ≈82.7% accuracy.
● CORE-Bench & research reproducibility — highest ≈21% on hard tasks.
● Evaluation framework limitations — cost, reliability, and benchmarks gaps.
Be the first to post comment!