
What if you could deploy software faster, with fewer bugs, and less manual work? That’s the promise of DevOps automation. By integrating development and operations through automated workflows, teams can focus on building, not babysitting processes.
In this post, I’ll cover the top DevOps automation tools in 2025. I’ll also explain what they do, why they matter, and how to choose the right ones for your stack.
DevOps automation is the process of using tools and scripts to automate tasks like:
It minimizes human error and speeds up deployment. According to Gartner, high-performing DevOps teams deploy code 46x more frequently than traditional teams.
Here’s what automation brings to the table:
DevOps without automation is just agile with extra steps.
Let’s dive into the key players across each category. I’ll also include their use cases, pros, and ideal scenarios.
Category: Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Why use Jenkins?
It’s the most widely used open-source CI/CD tool. Jenkins supports 1,800+ plugins and integrates with every major DevOps tool.

Pros:
Use case: Teams looking for flexibility and plugin support.
Category: CI/CD + Workflow Automation
Why use GitHub Actions?
It runs directly in your GitHub repository. Perfect for teams already using GitHub.

Pros:
Use case: Startups and open-source projects on GitHub.
Category: Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Why use Terraform?
It automates infrastructure provisioning on AWS, Azure, GCP, and more. Define your infra with simple configuration files.

Pros:
Use case: Companies scaling infrastructure across cloud providers.
Category: Configuration Management
Why use Ansible?
It's agentless and uses YAML. Ideal for automating server configurations, app deployments, and orchestration.

Pros:
Use case: Teams managing multiple environments (dev, QA, prod).
Category: Containerization
Why use Docker?
It packages your app and dependencies into a portable container. This ensures consistency across dev, staging, and production.

Pros:
Use case: Microservices-based applications.
Category: Container Orchestration
Why use Kubernetes?
It manages containerized applications at scale. Automates deployment, scaling, and management.

Pros:
Use case: Enterprise apps with multiple microservices.
Category: Monitoring & Alerting
Why use them?
Prometheus collects metrics, Grafana visualizes them. Together, they provide real-time insights and alerting.
Pros:
Use case: Observability in dynamic environments.
Category: GitOps
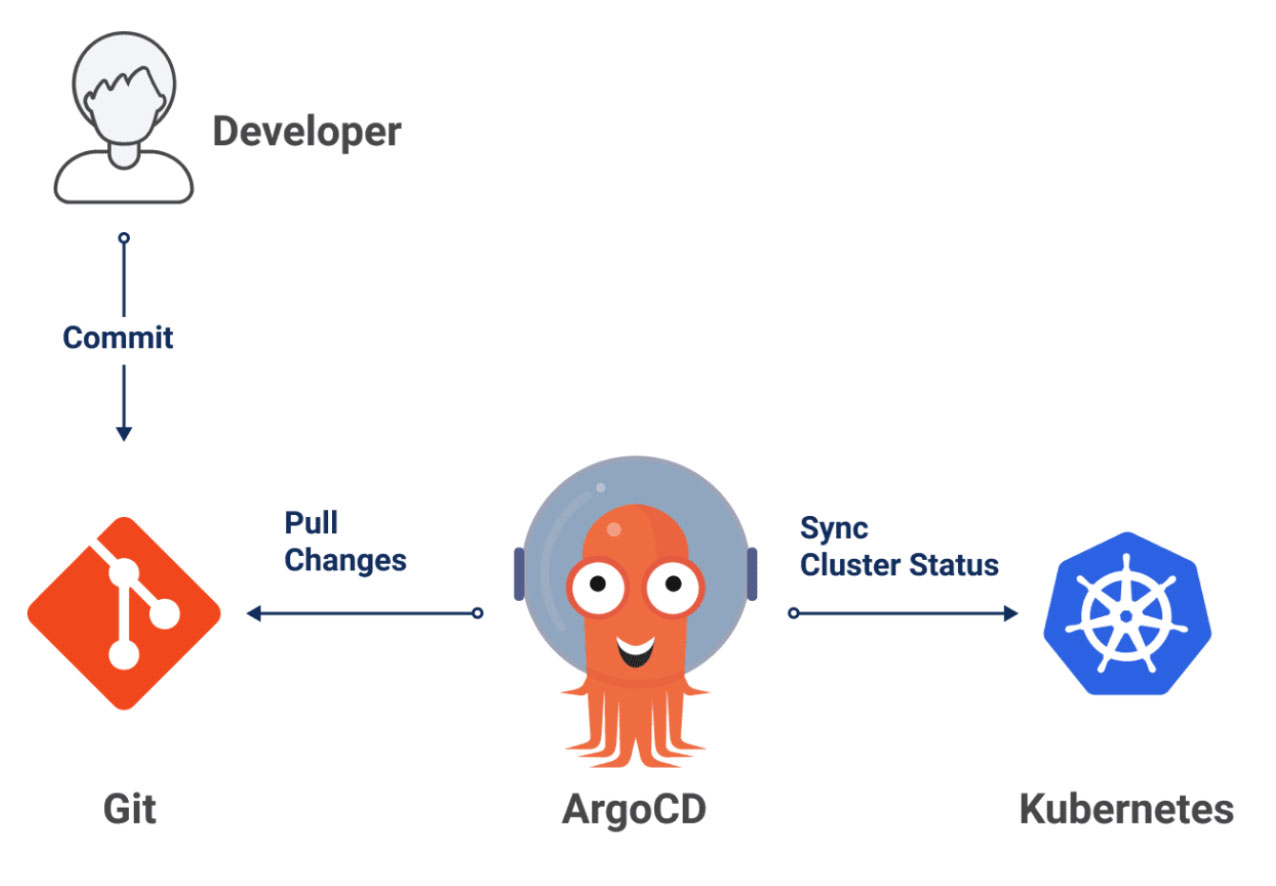
Why use Argo CD?
It automates Kubernetes deployments using Git as the source of truth.
Pros:
Use case: Kubernetes-native GitOps deployments.
Ask yourself these questions:
Tip: Start small. Integrate tools gradually. Monitor performance and bottlenecks.
These stacks evolve as needs change. Automation tools must remain flexible.
AI and ML are creeping into DevOps—think predictive incident response or self-healing infrastructure. Tools like Harness, Spacelift, and Firefly are already pushing this envelope.
Also, GitOps is gaining momentum. According to Red Hat, 60% of enterprises plan to adopt GitOps in 2025 (source).
DevOps automation isn’t about replacing humans—it’s about empowering them. With the right tools, teams ship faster, with fewer errors, and less burnout.
Start by identifying bottlenecks. Choose tools that align with your workflow. Iterate often.
Be the first to post comment!